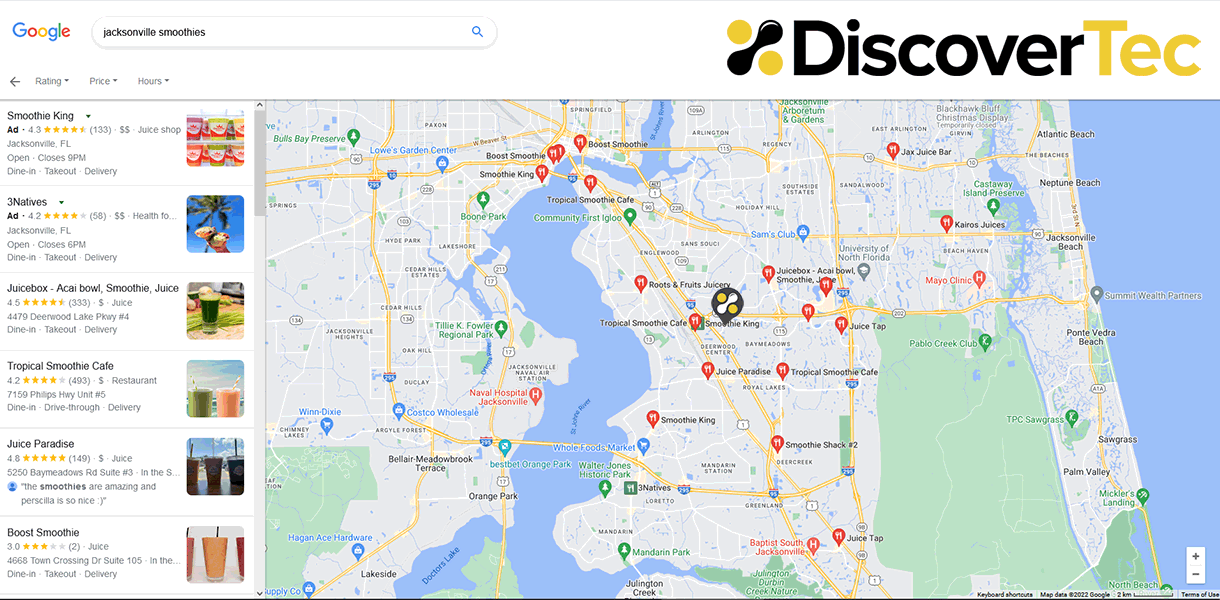
We all eat food. Sometimes once a day, sometimes three times a day, and often even more frequently. Tasty things like frittatas and smoothies. But the ways we order, receive, and pay for food from restaurants, grocery stores, eateries, and meal-prep companies has dramatically transformed because of the Covid pandemic. The same has happened with many other products and services that weren’t traditionally acquired digitally. Also, while some businesses are bringing people back to the office for work, some have made remote work permanent. So that means a lot of commuters who once saw your business on the way home and stopped by to shop, may not be anymore. Here is what you can do to help ensure they still find you, regardless of the lack of commute.
How does local search work?
Local search is about three main things:
- proximity
- relevance
- accuracy
Proximity means that your business is ready to sell to people who are physically nearby a given location. Relevance means that those people who are nearby are using the same search words online that you use to describe what your company sells. Accuracy in this context primarily means consistency across the web. These items shouldn’t change across the web, regardless of the advertising platform because that can cause both search engine and customer confusion:
- Business name and physical address
- Business phone number and contact information
- Business hours of operation
Location services help define proximity
There are three parts to proximity: the point, the zone, and the targets. When a customer uses their mobile phone, tablet, or computer to access the internet, their device is assigned a unique location, called an internet protocol (IP) address. When that customer performs a search, their question or phrase transmits to the search engine, and the results are returned to their device. This back-and-forth signaling passes both directions through a gate called location services software. For this example, we’ll refer to a customer as the target.
Similarly, your company’s website has a very specific definition of location. The location is whatever street address you define in your website’s underlying code (in the schema section - more about that later). For example, let’s say the address for Fast Fresh Frittatas is 123 Anywhere Drive, Great City, FL 34567. That address and zip code combination is the point, and it corresponds to specific Global Positioning System (GPS) coordinates. From there, the zone is the physical area surrounding the given point. We’ll use 5 miles for this example. That gives us a target, a point, and a zone.
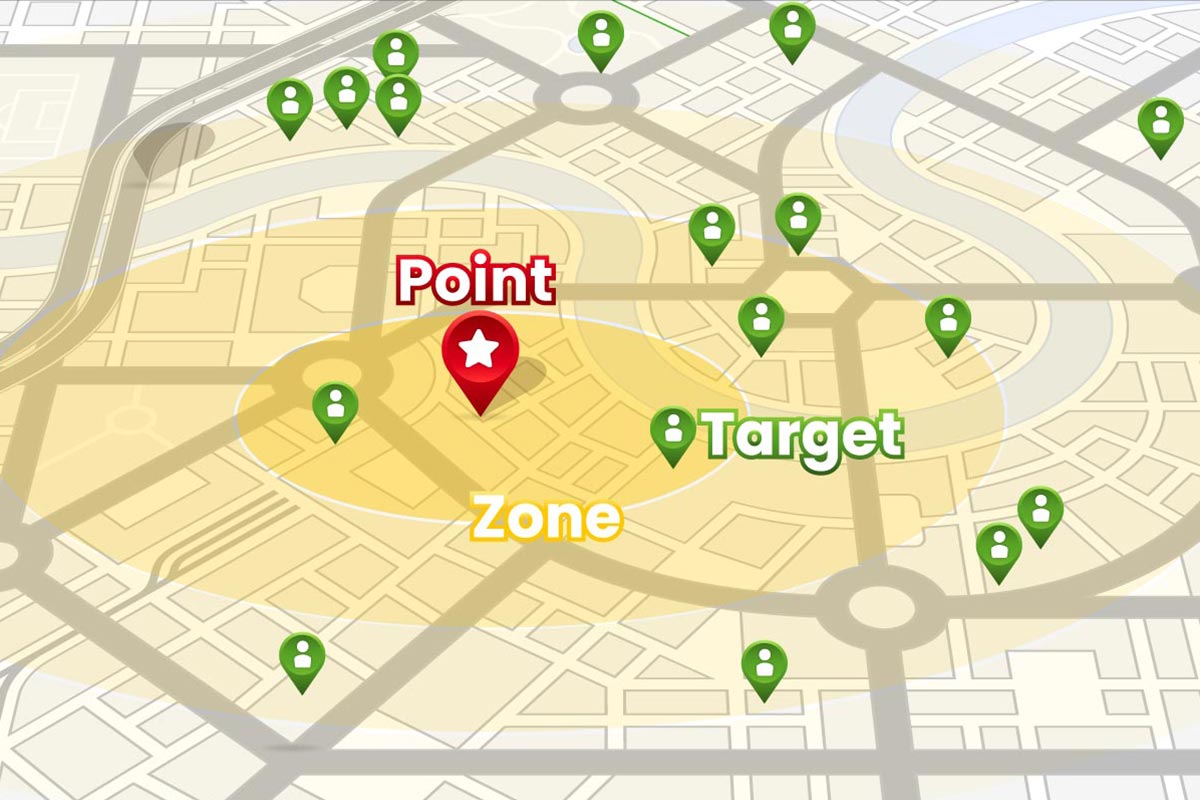
Now if the target enters a search phrase of “fresh frittata” into Google:
- while being physically located within 2 miles of the 34567-zip code,
- and their device’s location services are turned on
Then Fast Fresh Frittatas is more likely to appear on the Google Map search results, than a competing store called Fresh Frittatas & Tex Mex, located in the 32109-zip code. Location services determine this because the proximity of Fast Fresh Frittatas is closer to the target and is more likely to be what the customer is seeking.
The herd helps determine relevance
All local searches start with a customer entering a phrase into the search engine. When a target (customer who is in the zone of a given point) enters a phrase, they will be sent back a Search Engine Results Page (SERP). With Google search, some of the content categories of SERPs are All, Maps, Videos, Images and Shopping. With Bing search, there are also All, Maps, Images and Videos… as well as News and Work SERPs.
When that target customer clicks on the Fast Fresh Frittatas location in Google, they signal to the search engine that this may be exactly what they were looking for in zip code 34567. A moment or two later, a different target customer clicks Fast Fresh Frittatas. Then another target customer does it. Then another. And over time, more and more targets in zip code 34567 click on Fast Fresh Frittatas in the SERP, after searching for “fresh frittatas.”
This repetitive behavior tells Google that when the next target in the same zone looks for “fresh frittatas” they are most likely looking for Fast Fresh Frittatas. As a result, Google moves Fast Fresh Frittatas up the list of SERP websites to a higher ranking, so that people find them faster. This is an example demonstrating relevance in action.
Every local search term you can think of is constantly being weighed, compared, and returned to new customers. The ranking constantly changes, based on how many clicks have occurred within the same proximity with the same search phrase or keyword. If more targets begin to click on a Fast Fresh Frittatas competitor like Super Duper Fresh Frittatas, then very soon, the ranking will change to match the direction in which the herd is heading for frittatas. The search engine believes that the website everyone is heading to is the most relevant for the search term, simply because everyone is clicking that SERP link.
Relevance doesn’t stop with exact match phrases though. What happens when targets click on Fast Fresh Frittatas after searching for Mexican food? Or local fast eats? The same concept applies, where the search engine relates these other phrases with “fresh frittata” and starts to rank the website because of the indirect phrase association.
Consistent address and product information assures accuracy
What happens if there is more than one Fast Fresh Frittata in 34567? Each location should have a different address and unique business information in company listings, so that in smaller zones (1 mile, 2 miles, etc.) the results for a target’s search, point them to the closest store. If there are a dozen Fast Fresh Frittatas in Great City, FL and each has a different address, the system should work fine.
However, if there are a dozen Fast Fresh Frittatas in the zone, but they all share one address, it can cause confusion for search engines and the target customers. In this kind of situation, all searches would essentially show the initial or default location, even if a target was closer to a different location. It gets even more complicated if Fast Fresh Frittatas has inconsistent addresses listed in directories like Yelp or Trip Advisor which is why it is so important to maintain a consistent business name, address, and phone number (or NAP) when it comes to managing your online local business listings.
Use these six strategies to help local customers find you when they don’t leave home
Now that you understand the three major factors of local search optimization, these are strategies you can employ to help local customers find your location, even if they haven’t driven by recently. Some of this may seem like common sense but is often overlooked so be sure that your site has already implemented them.
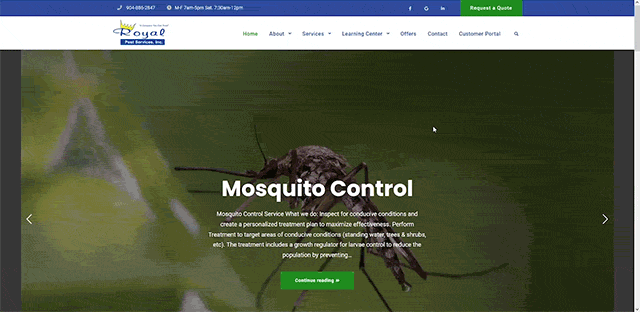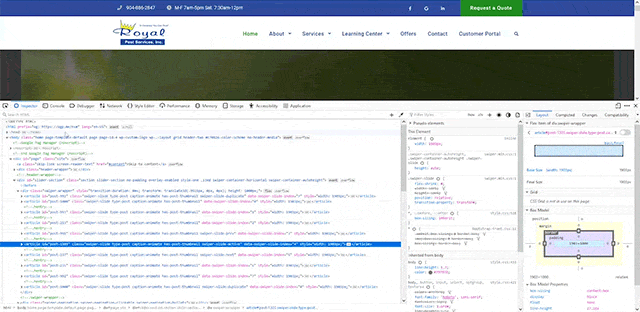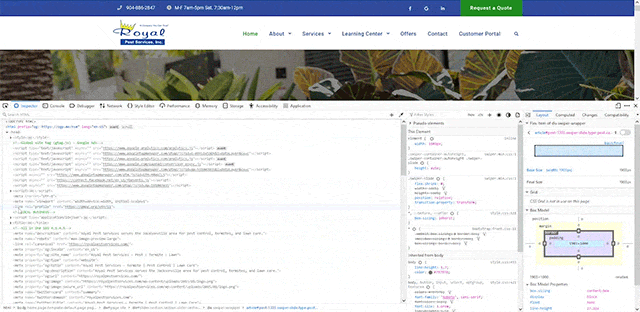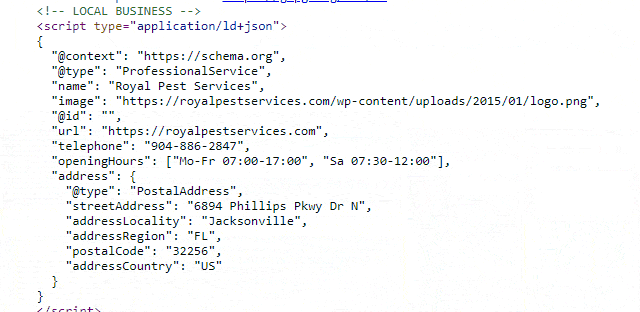
Ensure page schema is up-to-date and accurate, for speed
Search engine algorithms perform reviews of web pages on a periodic basis, and upon website owner request. If you have a website where you are adding new content or products on a monthly basis, then it’s advantageous to have Google and Bing crawl your site frequently. During each crawl of your pages, the software is trying to make sense of the content from a systematic perspective. Who, what, where, why, how – that’s essentially what schema is for your web pages, and what the crawlers need to interpret code at the fastest rate possible.
A lot of this is about speed. Search engines have signaled that they prioritize ranking of sites based on load times, responsiveness, and accessibility. Speed infers a higher quality customer experience in this context. So having the structural, topical, and other details on page content be accurate can only help match your pages to the search results desired:
- Start at top of the page and activate the page inspector
- Review the schema markup in the head (example shown above)
- Ensure that all the information in this markup also exists on the page, not just in the backend code
There are even schema checker tools you can use to make the process easier. By doing this, you are telling Google’s crawlers exactly what this is related to and are helping Google return better results, faster. Click here to learn more about how schema works.
Ensure page schema is up-to-date and accurate, for inclusion
Search engines also harness schema data to gather and disseminate broad audience content into areas of their results pages, called SERP features. There are numerous SERP features, all of which are built to return the correct categorical result to the searcher as quickly as possible without having to visit the website. Therefore, this type of content can be useful for local search optimization, to help drive traffic that is specific to the feature area. Try out these two search terms to see SERP features in action:
- Jacksonville show times (returns movie listings in Jacksonville, FL based on schema and location settings)
- Florida news (returns news article listings from across Florida, based on schema)
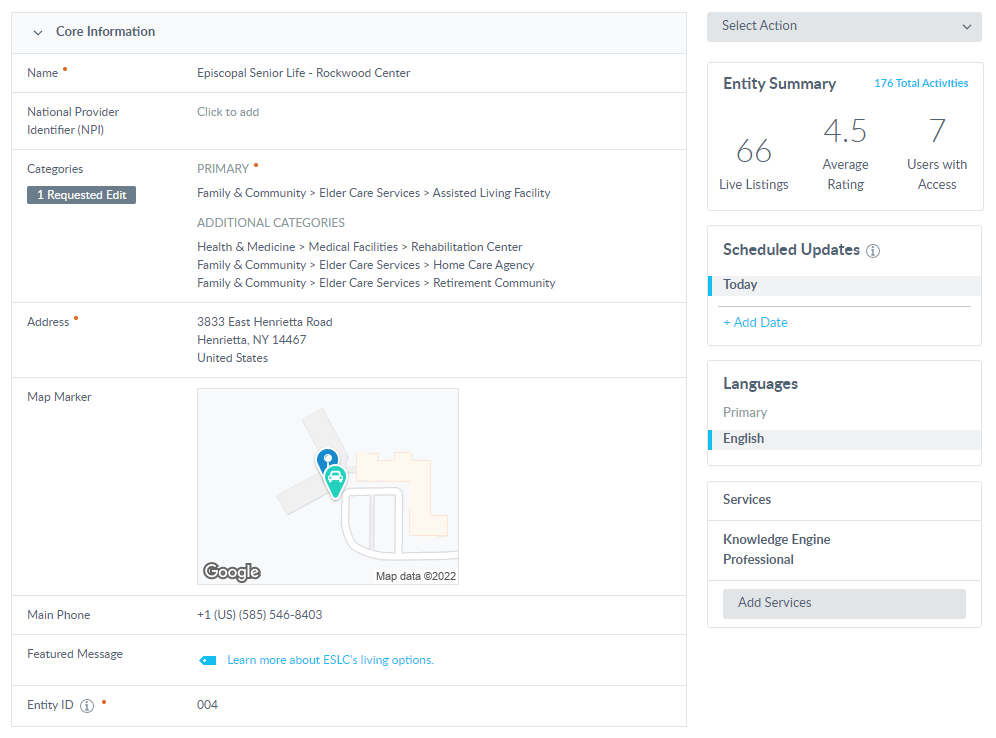
Keep that data clean
If you operate multiple locations, your website will likely have individual store nodes with their own address coordinates. When done correctly, each location will be optimized, easily searched, and found quicker within its given zone. When done incorrectly, people will not be able to easily find the exact location they are looking for based on their search.
Google My Business is a self-service tool for inputting your business information into Google’s systems, so that SERPs accurately reflect important details about your business. Start by creating an account and claiming your location information. Audit any existing information for each location and make sure they are all correct. Then ensure those addresses are matched correctly on all other directories that refer website traffic. Resolve any unclaimed profiles and validate any update requests that are factual so that you signal responsiveness to customer feedback. If it’s too difficult to do all of that one-by-one, consider implementing a tool like YEXT to automate and ease the process or seek the skilled online marketing team to help you better manage your local online presence.
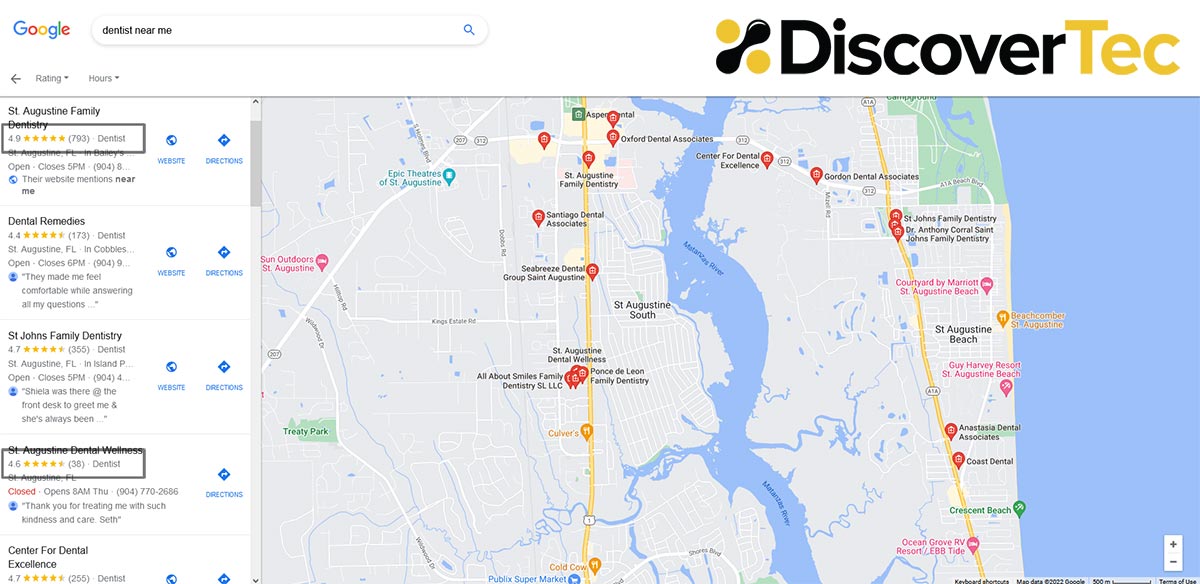
Leverage the herd mentality
If you compare two similar products in order to solve a problem, which of these would bring you more assurance:
- The product with thirty, 4-star reviews, or
- The product with three thousand, 4-star reviews?
Differing levels of consideration impact each buyer’s journey, but research has shown that online reviews influence decision-making.
Search engines use bots to review and collect data, so they just see clicks as clicks. Whether someone decides to click here or there is frequently influenced by an indirect status judgment. It may also be based on user assumptions about the size of a group who has rated something higher than something else. You may chalk that up to a safety-in-numbers mentality, or even a quality association based on volume. Either way garnering authentic ratings can help steer the herd in your direction. Therefore, pursuing a user reviews strategy in Google and other directories where you have locations and product information listed can only help you reinforce the search journey This will also help to improve local search results because of the indirect association of quality, based on the volume of positive reviews.
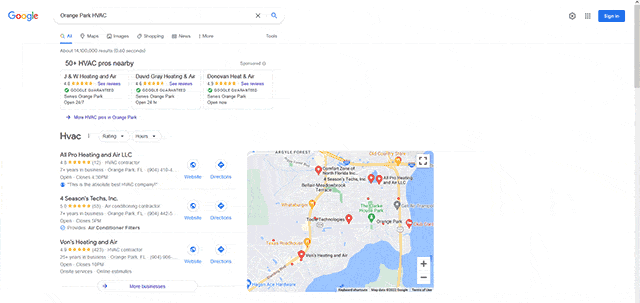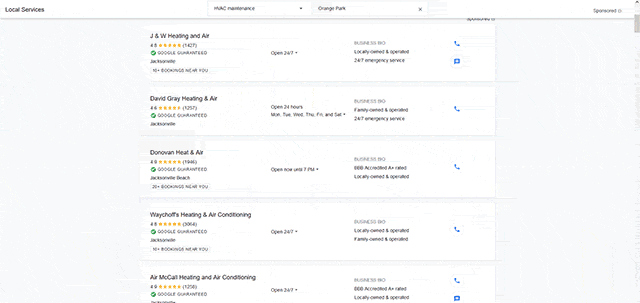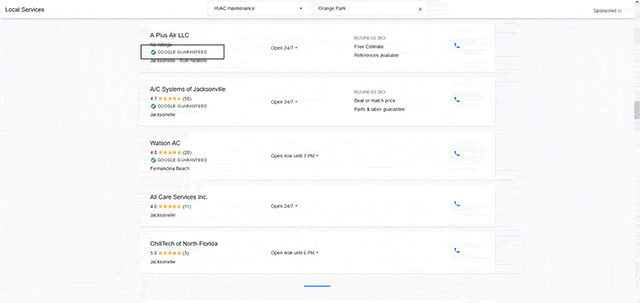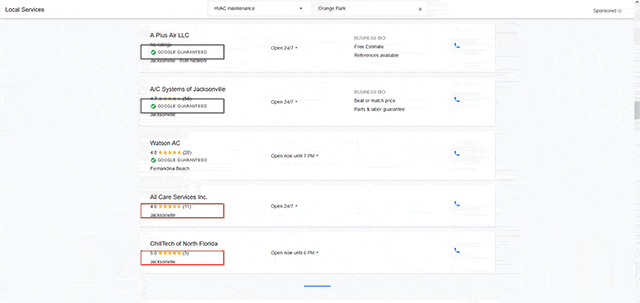
Enroll in Google Local Search Ads (LSA)
Depending on your business type, your products, and/or services, there may be several similarly named competitors in the area. So be sure to avoid adding duplicate/similar sounding company or product names of your own in the same vicinity. That way you avoid creating location confusion for search engines and consumers.
Also, look at premium listing services that tie into your local search strategy. For example, Google provides a local service provider advertising platform called Google Local Services Ads (LSA). Unlike regular keyword advertising, this search product is geared to hyper-local companies who provide in-home services (HVAC, plumbing, roofing, security, etc.). These listings appear at the very top of SERPs with two tiers of ad placement, and a Google Guarantees badge that reflects employee background screening performed by Google through Pinkerton.

Optimize product titles and facts for search
When you are looking for random consumer goods, where do you typically search – besides Google? If you replied, Amazon, this reflects how the e-commerce giant has positioned themselves as a product-fulfiller in the search realm. Shoppers who visit amazon.com to find what they want to buy outnumber the nearest competitor by over a 2:1 margin. Amazon has used title and description term stuffing to help drive this customer habit, where visitors frequently bypass Google altogether to search for their desired buys. Much of that happens because the same search terms would already return an Amazon product listing in Google meaning, website visitors are essentially cutting out the middleman to get what they want more quickly.
Google shopping ads do include features, facts, and definitions. If you are already listing products for sale on either Amazon, or Google, think about how your organic listings can maximize your advertising dollar. Are your website product listings sufficiently different from the competition? Are they inclusive of the common phrases someone searching for them will use? Think about what makes them especially attractive to someone searching locally and incorporate that listing strategy consistently throughout your marketing efforts so that you gain new visitors but avoid confusing search engines. An example of this would be the rise in pick-up and take-out/delivery options restaurants have now because of COVID.
Conclusion
By understanding how local search works, you can take steps to gain more online real estate and keep sales flowing through your website and make up for any loss of customers showing up on your doorstep. Once your business information is accurate and optimized for each target area or zone, the next step is to attract the attention of targets/customers most likely to buy. Read additional articles in our search series for tips on how to attract and draw online visitors who may be outside the proximity of your brick-and-mortar location(s).